Two China-linked advanced persistent threat (APT) groups have been observed targeting entities and member countries affiliated with the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) as part of a cyber espionage campaign over the past three months.
This includes the threat actor known as Mustang Panda, which has been recently linked to cyber attacks against Myanmar as well as other Asian countries with a variant of the PlugX (aka Korplug) backdoor dubbed DOPLUGS.
Mustang Panda, also called Camaro Dragon, Earth Preta, and Stately Taurus, is believed to have targeted entities in Myanmar, the Philippines, Japan and Singapore, targeting them with phishing emails designed to deliver two malware packages.
“Threat actors created malware for these packages on March 4-5, 2024, coinciding with the ASEAN-Australia Special Summit (March 4-6, 2024),” Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 said in a report shared with The Hacker News.
One of the malware package is a ZIP file that contains within it an executable (“Talking_Points_for_China.exe”), that when launched, loads a DLL file (“KeyScramblerIE.dll”) and ultimately deploys a known Mustang Panda malware called PUBLOAD, a downloader previously employed to drop PlugX.
It’s worth pointing out here that the binary is a renamed copy of a legitimate software called KeyScrambler.exe that’s susceptible to DLL side-loading.
The second package, on the other hand, is a screensaver executable (“Note PSO.scr”) that’s used to retrieve next-stage malicious code from a remote IP address, including a benign program signed by a video game company renamed as WindowsUpdate.exe and a rogue DLL that’s launched using the same technique as before.

“This malware then attempts to establish a connection to www[.]openservername[.]com at 146.70.149[.]36 for command-and-control (C2),” the researchers said.
Unit 42 said it also detected network traffic between an ASEAN-affiliated entity and the C2 infrastructure of a second Chinese APT group, suggesting a breach of the victim’s environment. This unnamed threat activity cluster has been attributed to similar attacks targeting Cambodia.
“These types of campaigns continue to demonstrate how organizations are targeted for cyber espionage purposes, where nation-state affiliated threat groups collect intelligence of geopolitical interests within the region,” the researchers said.
Earth Krahang Emerges in Wild
The findings arrive a week after Trend Micro shed light on a new Chinese threat actor known as Earth Krahang that has targeted 116 entities spanning 35 countries by leveraging spear-phishing and flaws in public-facing Openfire and Oracle servers to deliver bespoke malware such as PlugX, ShadowPad, ReShell, and DinodasRAT (aka XDealer).
The earliest attacks date back to early 2022, with the adversary leveraging a combination of methods to scan for sensitive data.
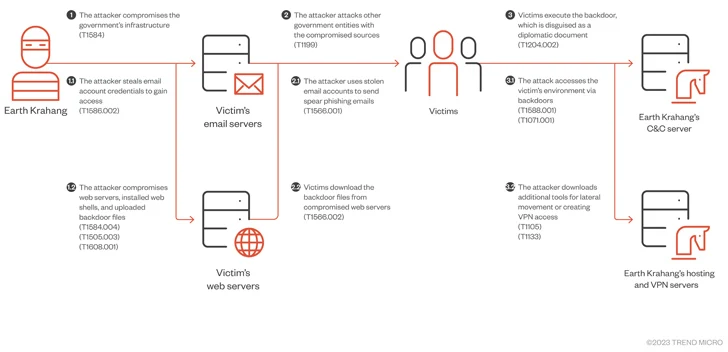
Earth Krahang, which has a strong focus in Southeast Asia, also exhibits some level of overlap with another China-nexus threat actor tracked as Earth Lusca (aka RedHotel). Both the intrusion sets are likely managed by the same threat actor and connected to a Chinese government contractor called I-Soon.
“One of the threat actor’s favorite tactics involves using its malicious access to government infrastructure to attack other government entities, abusing the infrastructure to host malicious payloads, proxy attack traffic, and send spear-phishing emails to government-related targets using compromised government email accounts,” the company said.
“Earth Krahang also uses other tactics, such as building VPN servers on compromised public-facing servers to establish access into the private network of victims and performing brute-force attacks to obtain email credentials. These credentials are then used to exfiltrate victim emails.”
The I-Soon Leaks and the Shadowy Hack-for-hire Scene
Last month, a set of leaked documents from I-Soon (aka Anxun) on GitHub revealed how the company sells a wide array of stealers and remote access trojans like ShadowPad and Winnti (aka TreadStone) to multiple Chinese government entities. This also encompasses an integrated operations platform that’s designed to carry out offensive cyber campaigns and an undocumented Linux implant codenamed Hector.
“The integrated operations platform encompasses both internal and external applications and networks,” Bishop Fox said. “The internal application is mainly for mission and resource management. The external application is designed to carry out cyber operations.”
The obscure hack-for-hire entity has also been implicated in the 2019 POISON CARP campaign aimed at Tibetan groups and the 2022 hack of Comm100, in addition to attacks targeting foreign governments and domestic ethnic minorities to gain valuable information, some of which are carried out independently on their own in hopes of landing a government customer.
“The data leak has provided rare insight into how the Chinese government outsources parts of its cyber operations to private third-party companies, and how these companies work with one another to fulfill these demands,” ReliaQuest noted.

Cybersecurity firm Recorded Future, in its own analysis, said the leak unravels the “operational and organizational ties” between the company and three different Chinese state-sponsored cyber groups such as RedAlpha (aka Deepcliff), RedHotel, and POISON CARP.
“It provides supporting evidence regarding the long-suspected presence of ‘digital quartermasters’ that provide capabilities to multiple Chinese state-sponsored groups.”
It also said the overlaps suggest the presence of multiple sub-teams focused on particular missions within the same company. I-Soon’s victimology footprint spreads to at least 22 countries, with government, telecommunications, and education representing the most targeted sectors.
Furthermore, the publicized documents confirm that Tianfu Cup – China’s own take on the Pwn2Own hacking contest – acts as a “vulnerability feeder system” for the government, allowing it to stockpile zero-day exploits and devise exploit code.
“When the Tianfu Cup submissions aren’t already full exploit chains, the Ministry of Public Security disseminates the proof of concept vulnerabilities to private firms to further exploit these proof-of-concept capabilities,” Margin Research said.
“China’s vulnerability disclosure requirement is one part of the puzzle of how China stockpiles and weaponizes vulnerabilities, setting in stone the surreptitious collection offered by Tianfu Cup in previous years.”
The source of the leak is currently not known, although two employees of I-Soon told The Associated Press that an investigation is ongoing in collaboration with law enforcement. The company’s website has since gone offline.
“The leak provides some of the most concrete details seen publicly to date, revealing the maturing nature of China’s cyber espionage ecosystem,” SentinelOne’s Dakota Cary and Aleksandar Milenkoski said. “It shows explicitly how government targeting requirements drive a competitive marketplace of independent contractor hackers-for-hire.”
